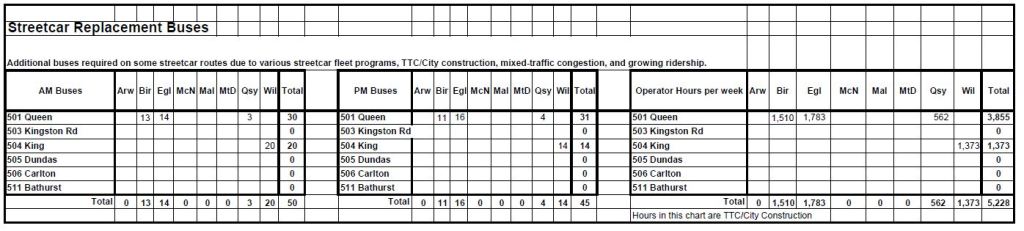
This article continues the review of the evolving travel times on current and proposed RapidTO corridors that started with Travel Times on RapidTO Corridors – December 2023 Update – Part I.
The routes covered here are:
- 60/960 Steeles West
- Finch Station to Pioneer Village
- Pioneer Village to Kipling
- 86/986 Scarborough
- 116 Morningside
- 905 Eglinton East Express
Introduction
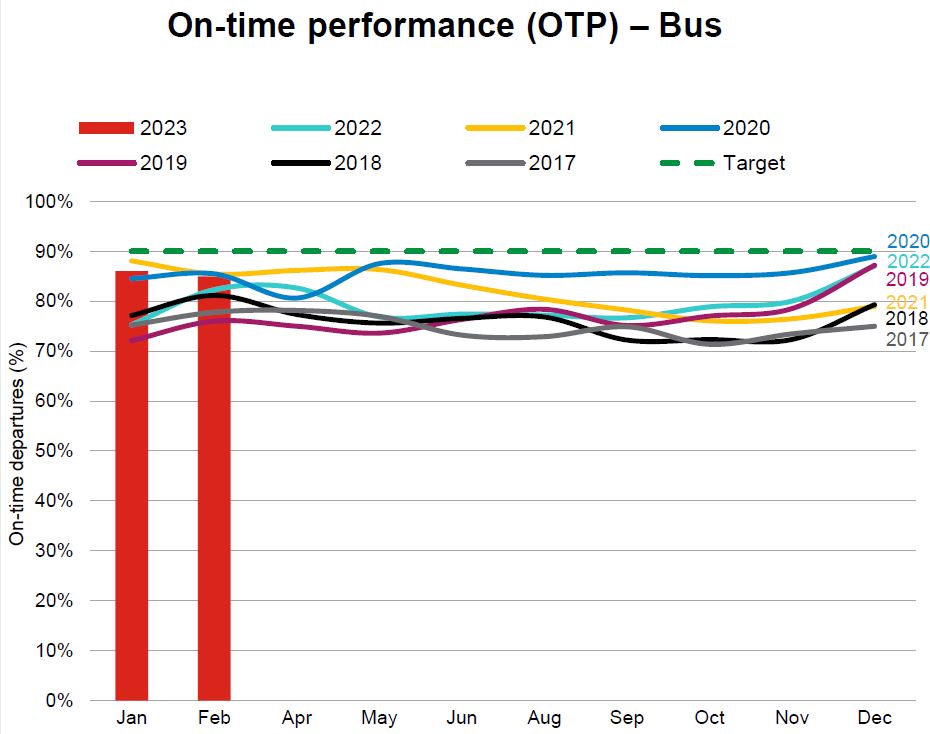
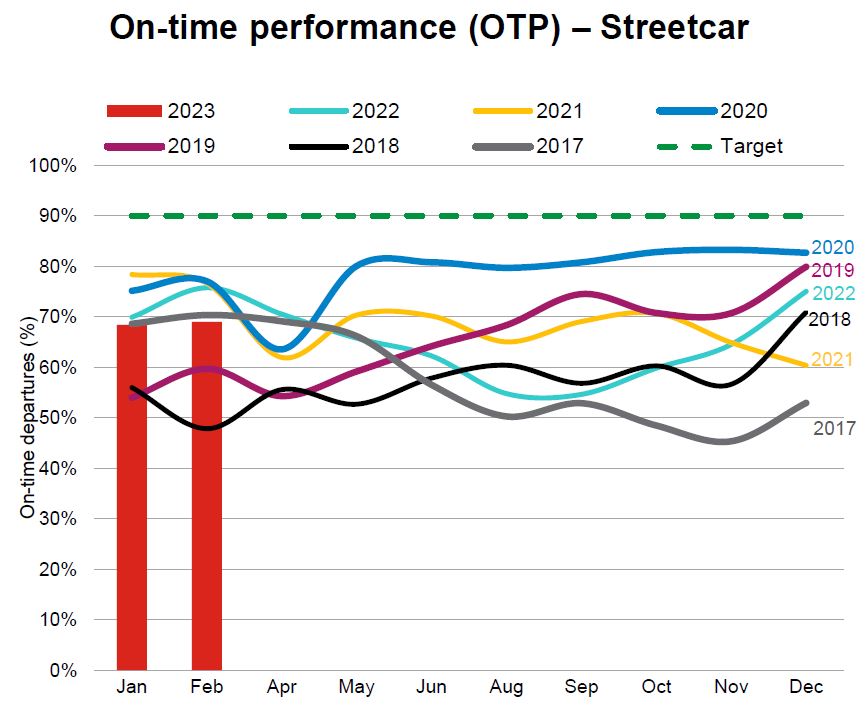
These charts are intended to show how travel times in many cases have been growing since the early days of the pandemic in March 2020. Where I have them, there is a small amount of pre-pandemic data for comparison.
In most cases, there is a notable drop in travel times in Spring 2020, with gradual growth thereafter. Drops for the year end holidays are common, but this was small in 2020 because isolation was still in effect. In 2021, there was a recovery followed by a combination of the drop for the holidays and the omicron wave. 2022 and 2023 saw bigger declines at the holidays. In some cases, the travel times in January 2024 are higher than the pre-pandemic values.
The Spring 2020 values are likely as good as one can expect from any transit priority scheme as they show the travel times of buses unencumbered by either traffic or heavy passenger loads.
Where the 85th percentiles (orange) spike well above the medians (blue), this shows the day to day variability in travel times that are particularly strong on Steeles West.
An important distinction lies in the location of time savings. Transit priority might not be present over an entire route, and a more detailed review of these data will show the locations of the critical segments. I have not included them here to avoid making an over-long article, but I will bring out more of that analysis as the City gets more deeply in route-specific studies.
A challenge for planners and traffic engineers is that the problem locations are likely to be the hardest to “solve” in the sense that they have the lease spare capacity, if any, to reallocate to transit. Conversely, there are areas where transit priority will make little difference because the road is uncongested most of the time, and signals are not a source of delay. Fine-grained study is essential to any new RapidTO plan.
In the first article of this pair, the charts ended at December 2023, but by the time I was working on this piece, the January 2024 data were also available and have been included.
In the case of routes already operating on red lanes in Scarborough (86/986 Scarborough, 116 Morningside and 905 Eglinton East Express), travel times have grown since 2020, but it is impossible to know how much they might have grown in the absence of transit priority measures other than by analogy to other corridors where conditions might not match.
Updated February 7, 2024: The charts for 116 Morningside have been updated to include data from late October to December 2020 that was omitted from the original version.
Continue reading