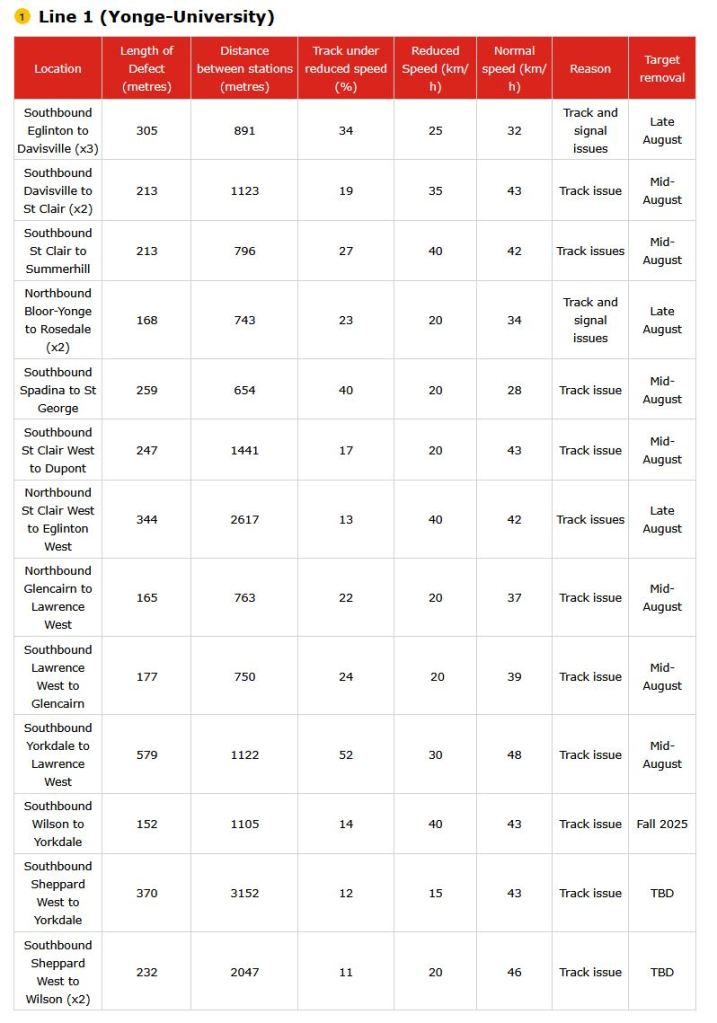
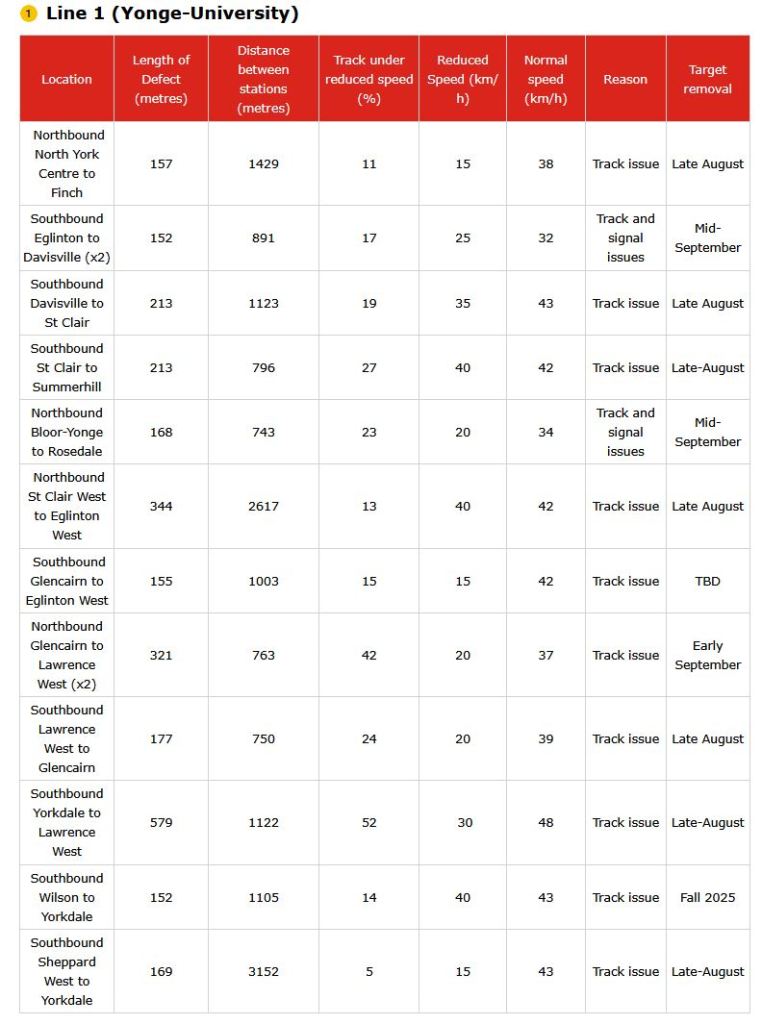
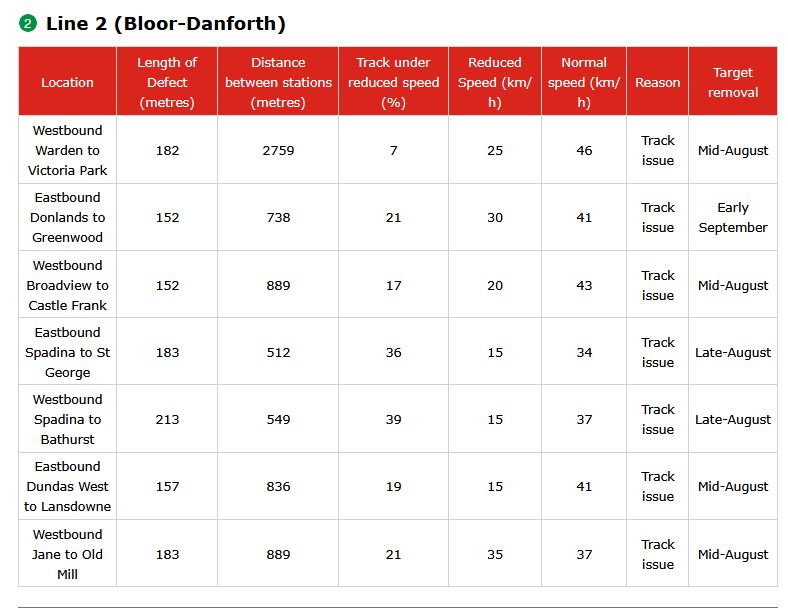
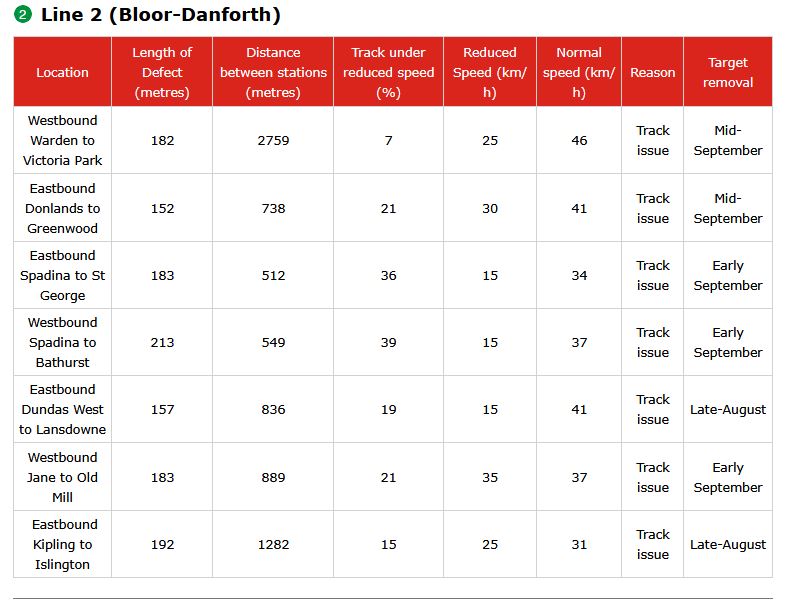
Tracking the costs of Metrolinx projects with publicly available data is not an easy task. They are a secretive organization, and present ongoing costs in a way that hides the eventual total cost of construction and operations. When anyone talks about “on budget”, there is no way to verify the claim because no overall budget figure is given for any project.
Instead, what we see are the cumulative value of contracts that have been awarded as well as spending to date. The rest, assuming that there even is a “budget”, is hidden on the grounds that telling would-be bidders how much money might be on the table will only encourage them to bid to that level. This is nonsense because, except for a few huge P3s, most projects are broken into many smaller contracts and knowing that there are billions available across a project’s allocation gives no hint of how much is earmarked for each component.
The situation is even more opaque in the case of contracts that mix design and construction (a finite capital cost) with operations and maintenance (an ongoing operating cost) over an extended period. Comparison with projects elsewhere is difficult because the components are not segregated.
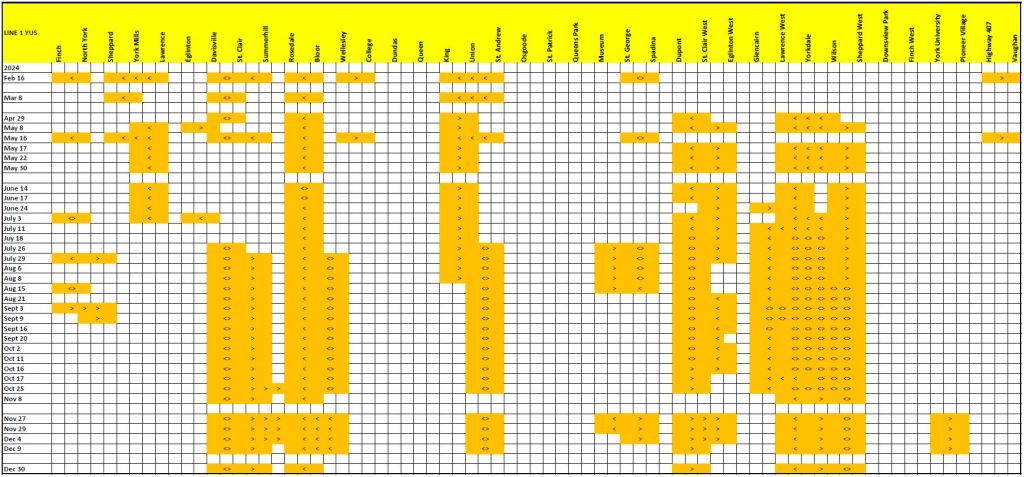
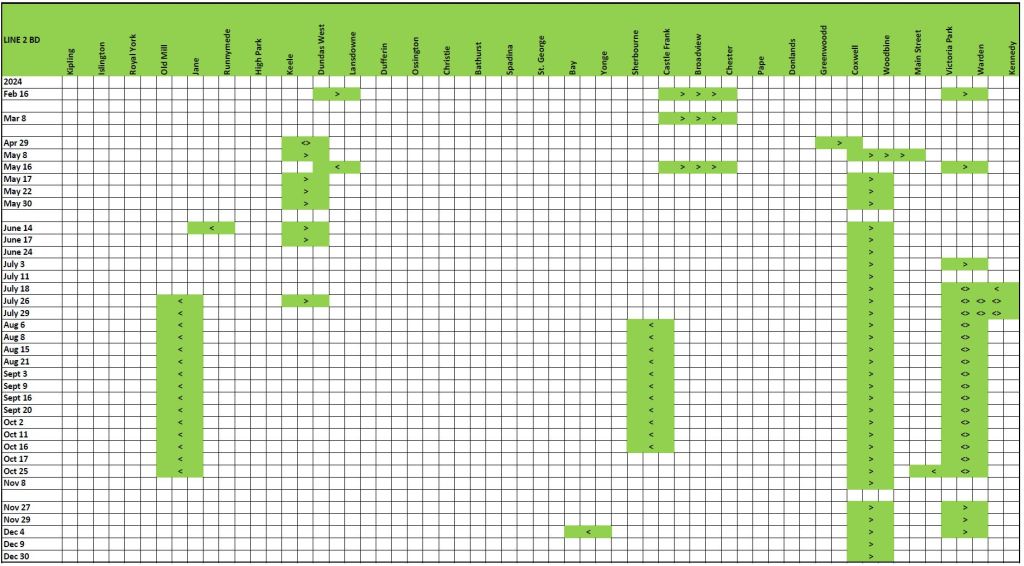
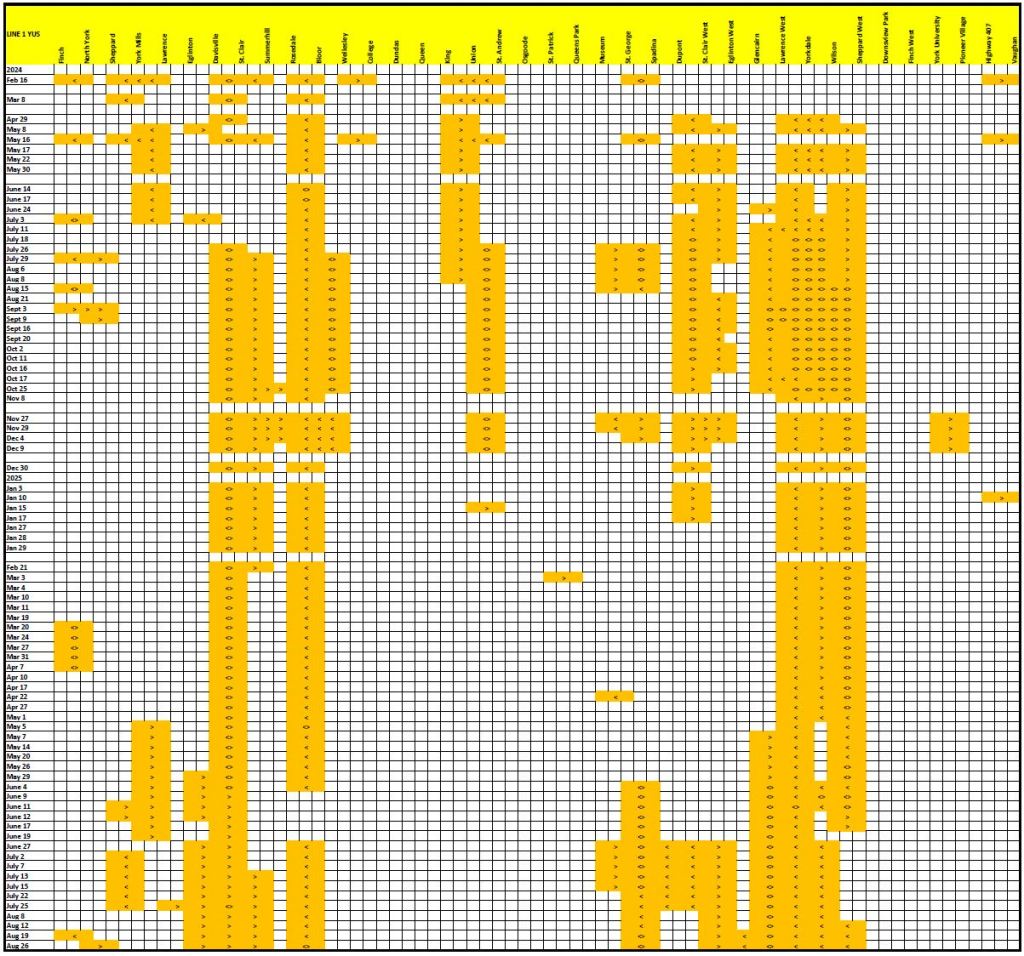
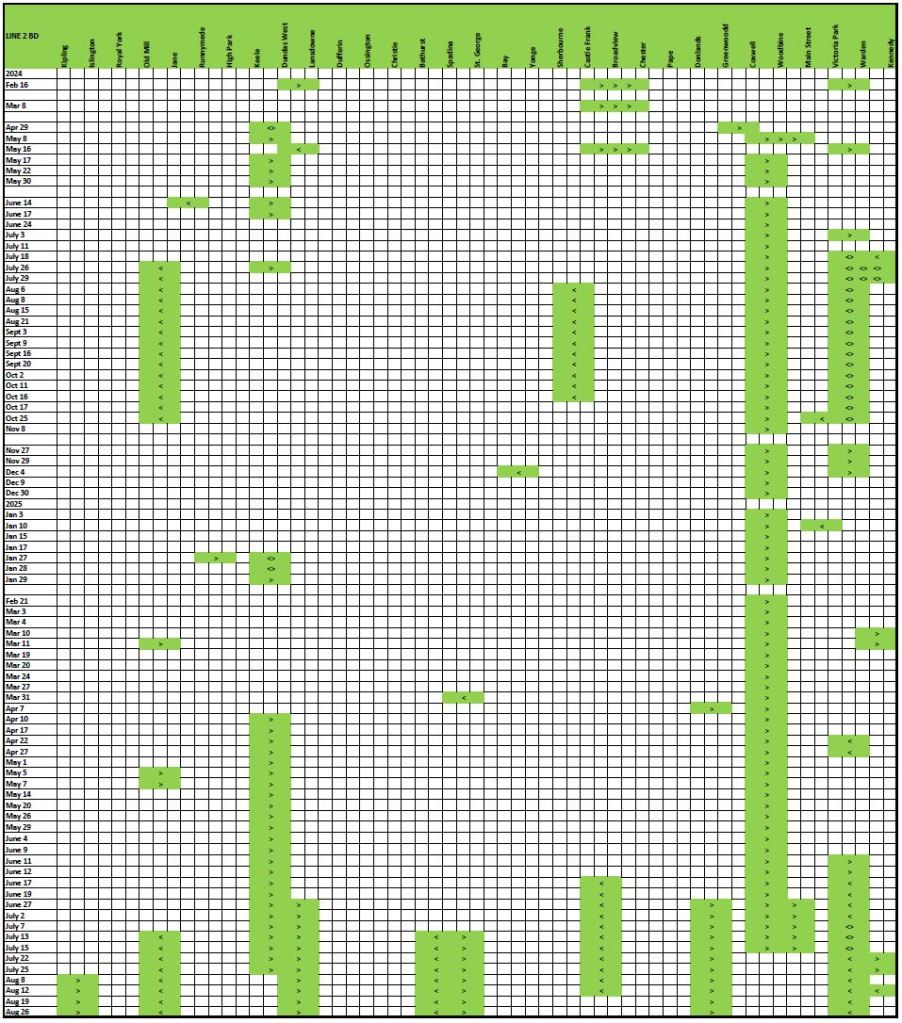
With the Eglinton and Finch projects now shifting from construction to operation, there is a chance to see what the split would be with the building largely complete. There will be some ongoing capital costs for project cleanup, but costs to date should largely represent the amount spent on the construction phase.
Many other projects are also in flight and there is no way to know if all of their components have been awarded and the values included in the “baseline” cost shown in financial reports.
This article consolidates the reported budgets, later renamed as “baselines”, as well as actual spending in the quarterly Metrolinx Capital Projects reports.
Some projects actually had projected in-service dates, at least in the early years, but these vanished long ago. Metrolinx promised big things once upon a time, but has been much slower to deliver, and at much greater cost than anticipated.
Continue reading