Ontario unveiled its 2025 budget on May 15. Although it speaks of “Approximately $61 billion over 10 years for public transit”, by far the lion’s share of this spending is for projects already underway in the construction and design stages.
All of this is for capital expansion and renewal, and nothing has been announced for day-to-day improvement of transit service.
GO Transit
The budget cites:
- The Hamilton-Niagara through service connection at West Harbour Station which is already in service.
- The proposed Bowmanville extension which has been announced before, but is only barely underway at the “early works” stage. This extension has physical alignment issues.
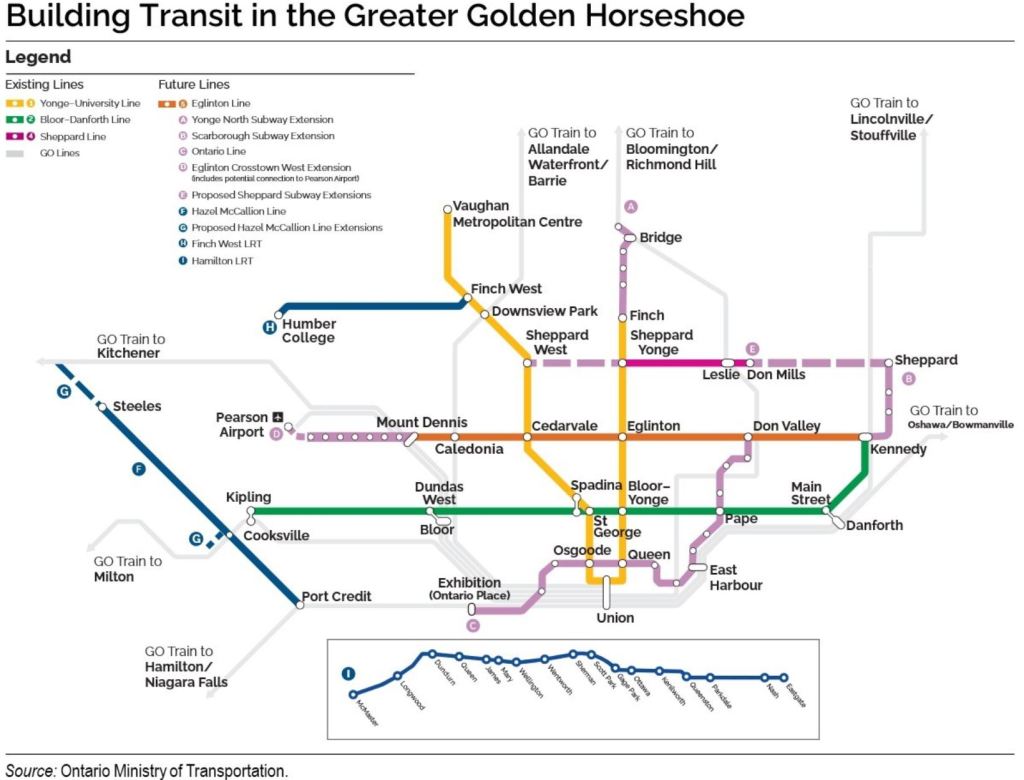
- GO 2.0 includes “delivering all-day, two-way service to Kitchener and Milton, building new GO stations across the region and advancing planning to unlock potential new rail corridors through midtown Toronto, Etobicoke, York Region and Bolton.” There are no dates attached, and some of these have been on maps for a very long time. Notable by its absence is any mention of electrification.
- A total of $850 million to refurbish GO Transit rail coaches at the Thunder Bay Alstom the North Bay ONR facility. This work is already announced. The cars may receive convenience upgrades such as “charging plug ports, cup holders and improved Wi-Fi”, but the long-term retention of these cars indicates that the operating model for GO electrification, if and when it occurs, will have a large component of locomotive-hauled trains rather than electric multiple units.
Subways
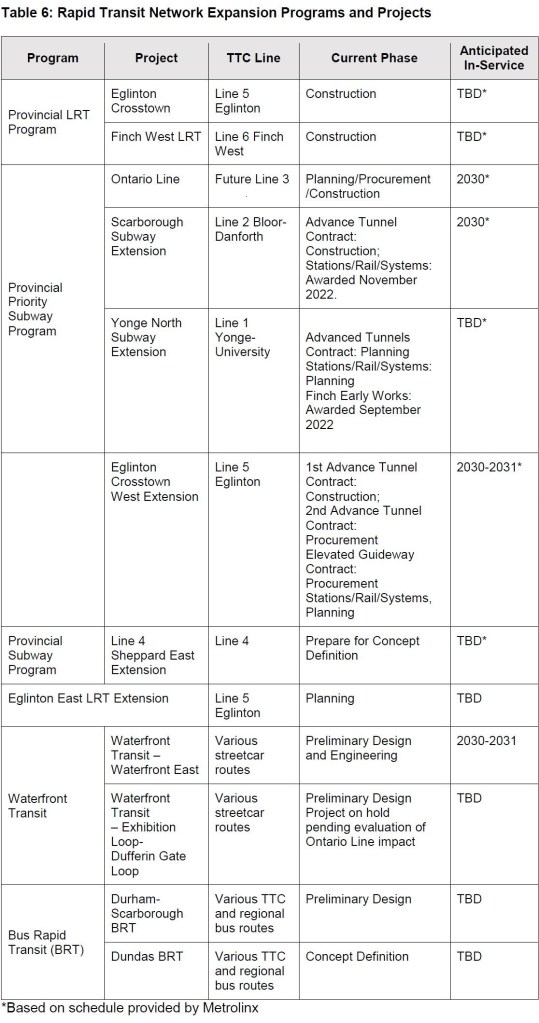
Subway projects in the budget are:
- Ontario Line (under construction).
- Eglinton-Crosstown Western Extension (under construction).
- Yonge North to Richmond Hill (procurement underway).
- Sheppard Subway Extension (planning, consultation and business case preparation underway). Notable in the map below is the absence of a line east of McCowan where there is a conflict with the City’s Eglinton East LRT project and with maintenance yard property requirements.
- New subway cars for Line 2. Provincial funding for these trains has been in place for some time. What is not yet funded are trains for service expansion beyond pre-covid 2019 levels. Trains for the Yonge North and Scarborough extensions are included in those projects. The TTC is in the Request for Proposals process for new trains, but this has been skewed by provincial statements that the work should go to Alstom’s Thunder Bay plant.
Yes, they seem to have forgotten the Scarborough Subway Extension (now under construction) in the text although it is included in the map below..
East Harbour Transit Hub
The hub at East Harbour Station, near the point where the Lakeshore East GO line crosses the Don River, will eventually serve GO Transit, the Ontario Line, and the local streetcar/LRT system via the Broadview Avenue Extension and a link west via Commissioners Street.
A substantial portion of this project is funded by the City of Toronto as a remnant of John Tory’s “SmartTrack” plan.
Light Rail Projects
- Hamilton LRT: This is in early states with procurement underway for Civil Works and Utilities.
- Hazel McCallion (Mississauga) LRT: Construction is well underway for the initial phase of this project, and the Province is studying whether the extension into downtown Brampton should be tunneled.
- Ottawa LRT: The Province is studying a potential upload of the Ottawa LRT “to help reduce costs for Ottawa taxpayers”. What implications this might have for future network operation and expansion is not clear.
- Eglinton Crosstown and Finch West LRTs: “Major construction for both projects is now complete. Metrolinx continues to focus on safety and operational readiness testing, as the projects advance toward revenue service.” There is still no commitment to opening dates, and we are getting close to the three-month lead-time required for a go/no-go decision for an early fall 2025 start of service. Meanwhile, TTC has begun the process to update subway train announcements and maps to reflect the new lines.’
- There is no mention of the Eglinton East or Waterfront East projects. In a recent letter, Mayor Chow asked the Federal government to contribute 1/3 to these schemes, but there is no indication of support in the Provincial budget.